Direkte Laryngoskopie vs. Indirekte Laryngoskopie: Unterschiede und Vorteile
Sep 24, 2024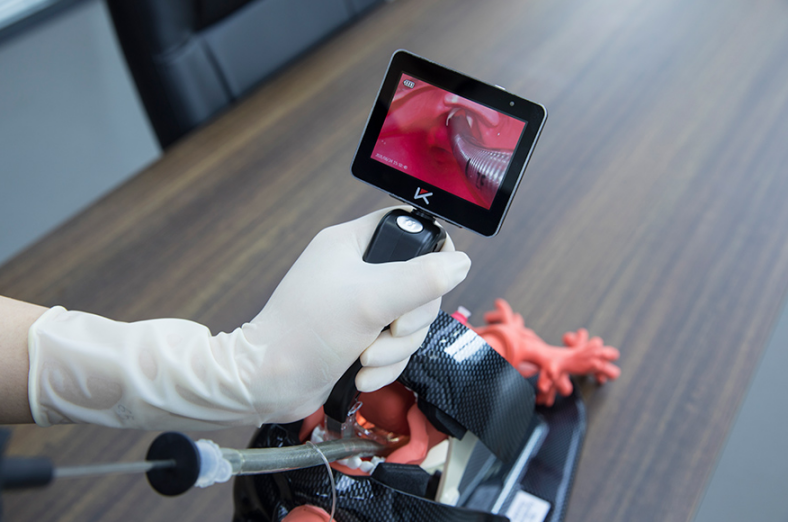
When focusing on the visualization of the larynx, as well as carrying out essential procedures such as intubation, medical practitioners generally rely on two predominant techniques: direct laryngoscopy (referred to as Direkte Laryngoskopie) and indirect laryngoscopy (referred to as Indirekte Laryngoskopie). These two methodologies, while similar in their ultimate goal of observing the laryngeal structures, diverge considerably in their procedural approach, their degree of invasiveness, and the range of applications for which they are suited.

Each method brings its own distinct set of benefits, making them applicable to different clinical scenarios depending on the needs of the patient and the healthcare setting. A clear understanding of these differences and the respective advantages of each technique equips medical professionals with the ability to make the most informed decisions for patient care. This discussion delves into the key distinctions between direct and indirect laryngoscopy, highlights their respective advantages, and provides insights into the most suitable contexts for their application.
Direkte Laryngoskopie: Definition and Practical Uses
The procedure known as Direkte Laryngoskopie involves the deployment of a laryngoscope, a highly specialized instrument, enabling the physician to visualize the larynx and vocal cords directly. During this process, either a rigid or a video-assisted laryngoscope is passed through the patient’s mouth, allowing for real-time observation of the vocal cords. The procedure is frequently implemented in emergency situations, during the induction of anesthesia, or in instances where meticulous control is required, such as in endotracheal intubation.
Unobstructed and Immediate Visualization
One of the standout advantages of direct laryngoscopy is its capacity to afford an unimpeded, clear view of both the vocal cords and the trachea. This capability is particularly critical in procedures such as intubation, where precision is paramount in order to prevent trauma to the airway. For example, Mole Medical, a prominent provider of high-quality laryngoscopic equipment, offers portable laryngoscopes equipped with high-intensity lighting systems. These devices deliver outstanding clarity, enabling medical personnel to perform intubations with greater speed and safety.
Flexibility in Emergency Environments
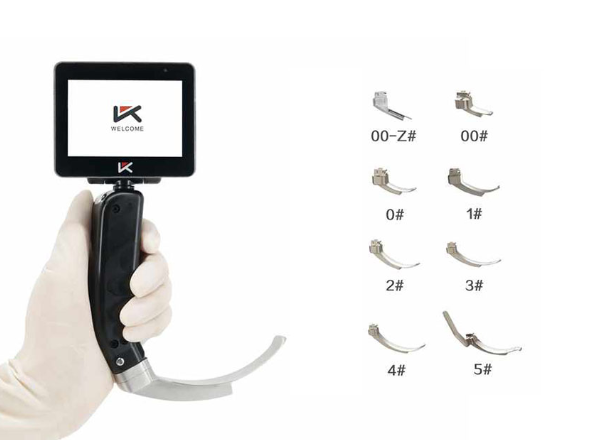
Direct laryngoscopy is widely regarded as highly effective in urgent medical contexts such as the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU), as well as in departments dealing with respiration and anesthesia. The ability to visualize the airway directly makes this method particularly well-suited for critical situations that demand rapid intubation. Mole Medical’s portable laryngoscope, which features three reusable blades, represents an exemplary model of versatility. Its compact design not only facilitates ease of use but also ensures that healthcare providers can perform intubations even in challenging environments, such as during patient transport or in the field, where precision and quick response are vital.
Comprehensive Blade Compatibility for Varied Anatomies
Among the notable features of direct laryngoscopes, such as those offered by Mole Medical, is their compatibility with a wide range of blade sizes and styles. This adaptability allows for the effective use of the laryngoscope across patients with differing anatomical needs, ranging from neonates to fully grown adults. Constructed from medical-grade 316 stainless steel, these blades are designed for durability and hygiene, allowing for repeated sterilization and use, thus ensuring patient safety while maintaining cost-efficiency for medical institutions.
Indirect Laryngoscopy: Definition and Clinical Uses
In contrast to the direct approach, indirect laryngoscopy utilizes either a mirror or a fiber-optic scope to visualize the larynx, thereby eliminating the need for the insertion of a rigid instrument into the patient’s oral cavity. This technique is more commonly employed in non-emergency settings, such as during outpatient examinations in ear, nose, and throat (ENT) clinics, where a less invasive method is preferred. By reflecting light off a mirror placed at the back of the throat, or using a fiber-optic camera, this method enables the clinician to observe the vocal cords and adjacent structures.
A Minimally Invasive Approach
A key benefit of indirect laryngoscopy lies in its minimal invasiveness. Unlike direct laryngoscopy, which requires the insertion of a laryngoscope, indirect methods are typically more comfortable for the patient, as they do not necessitate the introduction of a large instrument into the throat. This method is particularly well-suited for routine assessments in patients who are awake and conscious, especially for those who may not tolerate the discomfort of a direct laryngoscopy. Conditions such as vocal cord polyps or minor laryngeal dysfunctions can be diagnosed with relative ease using this approach, particularly in outpatient settings.
Greater Comfort for the Patient
Another notable advantage of indirect laryngoscopy is the enhanced comfort it offers to the patient. Typically performed with the patient seated in an upright position, this method avoids the need for anesthesia or sedation, making it a convenient option for evaluating patients presenting with milder symptoms such as voice changes or throat discomfort. However, it should be noted that while this approach provides a more comfortable experience, it may not deliver the same level of visual clarity as direct laryngoscopy, particularly in complex cases.
Ideal for Non-Urgent Diagnostics
Given its less invasive nature, indirect laryngoscopy is particularly advantageous in non-emergency situations, where the physician may need to assess the laryngeal structures without resorting to sedation or intensive monitoring. Although it lacks the precision required for procedures such as intubation, it is nonetheless an excellent choice for rapid, low-risk evaluations, where a quick assessment of the vocal cords is sufficient.
Major Distinctions Between Direct and Indirect Laryngoscopy
Despite their shared goal of visualizing the larynx, direct and indirect laryngoscopy differ significantly in terms of their methodology, the degree of patient comfort they afford, and their overall complexity in clinical application.
Degree of Invasiveness
Direct laryngoscopy is an inherently more invasive procedure, often requiring the use of anesthesia or sedation, particularly in patients with heightened sensitivity to discomfort. By contrast, indirect laryngoscopy is far less invasive and can generally be performed in a clinic without the need for sedation. The choice between the two is largely dictated by the clinical objective and the condition of the patient.
Clarity of Visualization
The level of clarity provided by direct laryngoscopy is superior, offering a more precise and direct view of the laryngeal structures, making it the preferred choice for procedures such as intubation or surgical interventions. On the other hand, indirect laryngoscopy, while providing a broader view, may lack the precision required for more intricate procedures, making it more suited for general assessments.
Equipment Complexity and Usage Settings
The instruments used in direct laryngoscopy, such as those supplied by Mole Medical, are generally more sophisticated, featuring advanced lighting systems and blade compatibility options designed for use in emergency and surgical environments. Indirect laryngoscopy, however, relies on simpler tools like mirrors or fiber-optic scopes, making it better suited for routine outpatient diagnostics.
The Advantages of Video Laryngoscopy
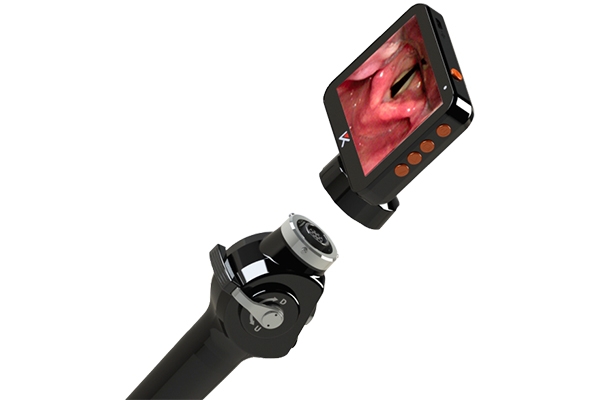
In recent years, video laryngoscopy has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation within the domain of direct laryngoscopy. Devices like the video laryngoscope offered by Mole Medical seamlessly integrate direct visualization with enhanced video capabilities, allowing for a wider, more detailed view of the larynx while minimizing disturbance to the surrounding tissues.
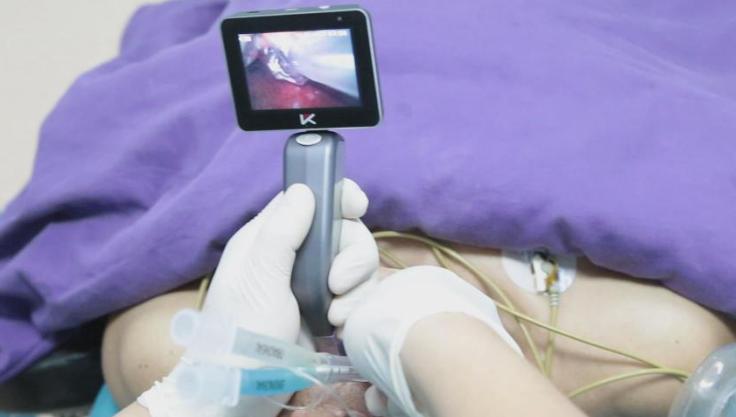
Enhanced Visual Clarity and Expanded Viewing Angle
The Mole Medical video laryngoscope features a 70° viewing angle, ensuring that the glottis remains fully visible throughout the intubation process. This broader perspective not only enhances procedural accuracy but also helps to prevent complications, particularly in cases involving difficult airways.
Advanced Anti-Fogging Technology
A notable feature of modern video laryngoscopes is their integrated anti-fogging technology. Devices such as the one provided by Mole Medical include an instant-activation anti-fog system that ensures the lens remains clear without requiring preheating, providing uninterrupted visibility throughout the procedure.
Versatility for Diverse Clinical Needs
Mole Medical’s video laryngoscope is compatible with a variety of blade sizes and styles, making it suitable for use across a broad spectrum of patients, from neonates to adults. Additionally, its rotating monitor allows clinicians to intubate from a range of angles, enhancing the device’s utility in complex clinical scenarios.
Conclusion
While direct and indirect laryngoscopy each have their own distinct set of advantages, the choice of method depends largely on the clinical context and patient needs. Direkte Laryngoskopie, particularly when augmented with video technology, offers superior clarity and precision, making it indispensable in emergency and surgical settings. Meanwhile, indirect laryngoscopy, with its minimally invasive approach, remains a key tool for non-emergency diagnostics. Both methods play an essential role in modern medical practice, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care based on their condition.
Categories
Latest Articles

Affordable Bronchoscope: Price, Features, and What to Expect
The Role of Bronchoscopes in Modern Medicine A bronchoscope is an important medical tool. Doctors use it to look inside the lungs and airways. It helps diagnose infections, tumors, and other lung problems. It is also used to remove blockages and take tissue samples. Hospitals and clinics rely on bronchoscopes for many procedures. A clear ... Read more

Laryngoscope mole Fiber optic: A Clearer View, A Safer Airway
The Laryngoscope mole Fiber optic is a tool for airway management. It helps doctors see inside the throat. It has a fiber optic system that gives a bright and clear view. Doctors use it to guide breathing tubes into the airway. It makes intubation easier and safer. This laryngoscope works with different blades. The Miller blade ... Read more

CE Get√ Disposable bronchoscope and Disposable uroscope!
CE Get√disposable bronchoscope and disposable uroscope!Factory direct sales. Welcome to inquire. OEM is available.

Mole Medical invites you to meet at Expomed Eurasia 2025
Mole Medical invites you to meet at Expomed Eurasia 2025 Mole Medical sizi Expomed Eurasia 2025'te buluşmaya davet ediyor

Mole Medical invites you to meet the 91st China International Medical Equipment Fair (2025 Shanghai CMEF)
Dear partners at home and abroad:In the era of the booming development of global Medical technology, Mole Medical has always adhered to the original intention of innovation, and made intensive efforts in the field of medical endoscopes, constantly making technological breakthroughs and developing high-quality products. On this occasion, we cordially invite you to attend the ... Read more



